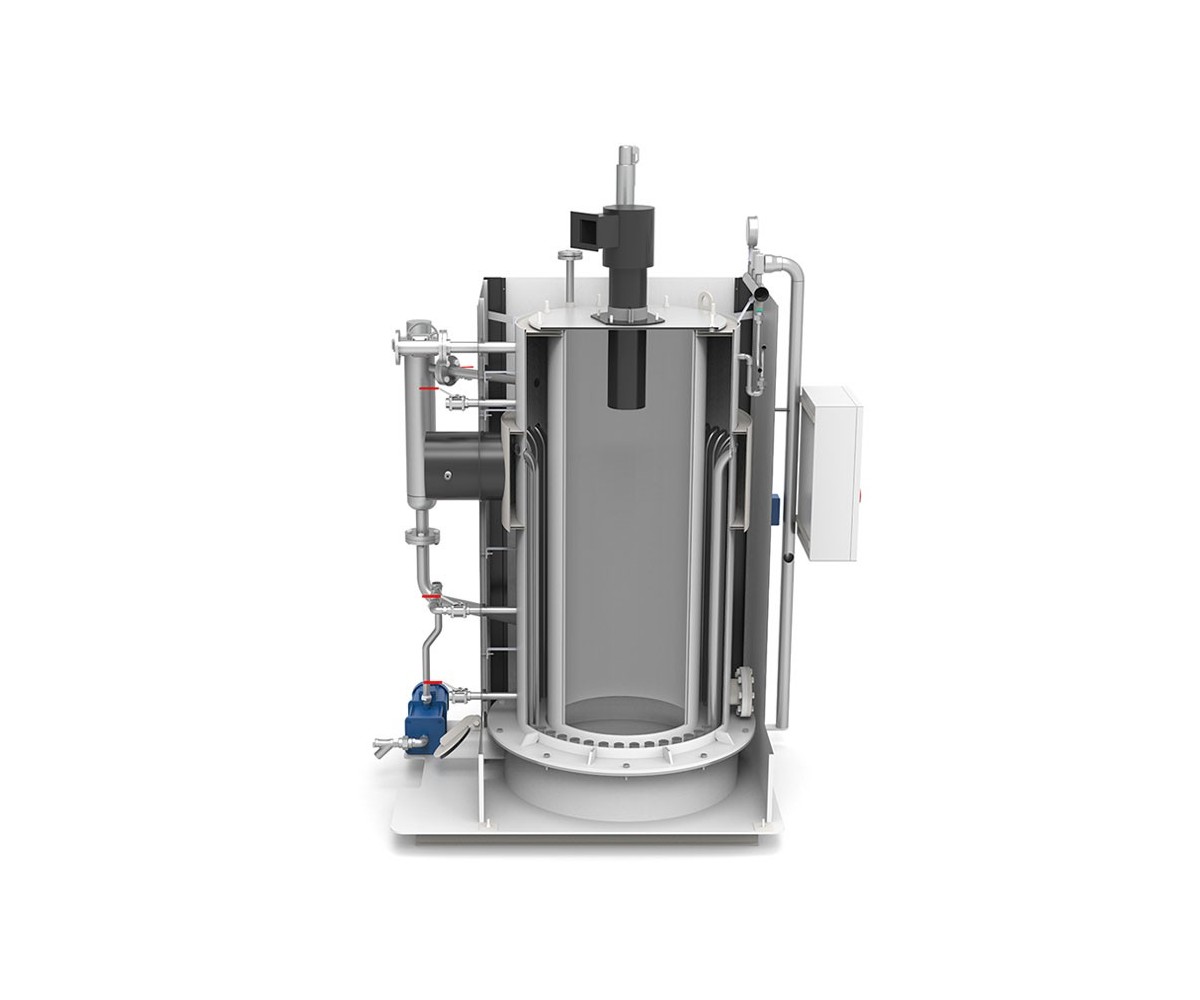
Cold Start in Steam Installations

Cold Start-Up and Water Hammer Prevention Methods
What is the best solution to prevent water hammer in steam lines during cold start-up and long-term stand-by without steam draw?
To prevent water hammer in steam lines during cold starts or long periods of no-load conditions, it is crucial to focus on the design, operation and maintenance of the steam system. Here are the best solutions:
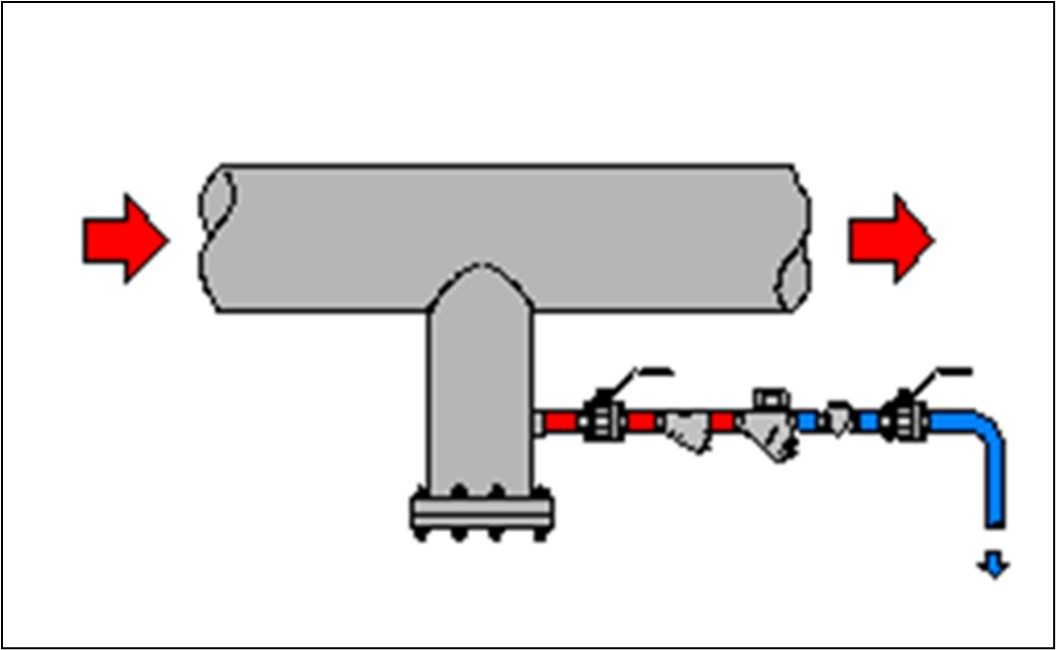
1. Condensation Drainage - Make Drain Pockets and Install Steam Trap
Drain the condensate accumulated during start-up and operation with Thermodynamic Traps placed in the drain pockets at every 30 to 50 meters (including rising/falling elbows). Be sure to return the condensate to the condensate tank. Check and maintain the traps regularly to ensure they are functional and that they remove the condensate effectively.
2. Slow and Controlled Heating - Gradual Heating
Start the steam flow gradually to ensure even heating of the pipeline and surrounding components, thus minimizing thermal stress and sudden condensation. You can use the bypass lines of the control valves to slowly preheat the system before starting the full steam flow.
3. Slope and Proper Pipe Design - Correct Pipe Slope
Ensure that steam lines are sloped (usually 1:70) in the direction of the process so that condensed condensate can flow into the traps or drains.
Don't forget to put metal expansion joints to accommodate thermal expansion and prevent stress on the lines.

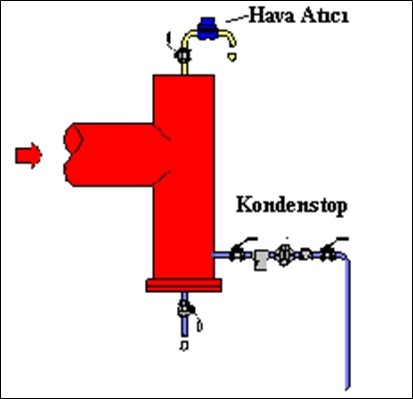
4. Air Evacuation from the End of the Installation
Place an air vent at the end of the line to remove air, which is an important component that prevents heating. Otherwise, air can prolong condensate discharge and increase the risk of water hammer.
5. Insulation - Proper Insulation of Steam Lines
Use high-quality thermal insulation to reduce heat loss and condensation in steam lines when there is no steam draw.

6. Install the Separator
By installing separators on boiler main lines and distribution main lines, you can eliminate the effects of sudden water accumulation and water splashes by increasing steam efficiency and quality without wet steam or water entrainment.

By following these practices, you can effectively prevent water hammer and ensure safer and more efficient steam system operation during cold starts and extended no-load conditions.